Basic single sign on in Laravel
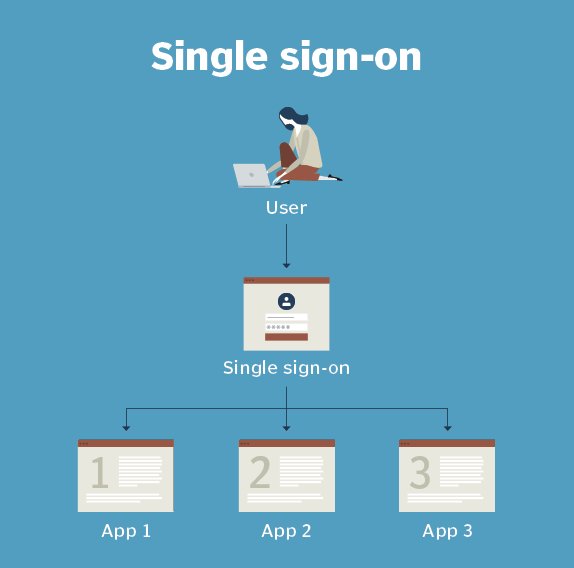
Great! Laravel provides a built-in authentication system that can be used for single sign-on (SSO) purposes. Here's a high-level overview of how you can implement SSO in Laravel:
1. Install the necessary packages:
You will need to install the following packages in your Laravel project:
laracasts/auth- This package provides the basic authentication functionality for Laravel.tymondesign/jwt-auth- This package provides JWT (JSON Web Tokens) authentication, which is a popular method for implementing SSO.
2. Set up the authentication system:
In your config/auth.php file, you will need to define the authentication drivers that you want to use. For example:
'providers' => [
// Google Auth
App\Providers\GoogleAuthProvider::class,
],
3. Create a custom authentication provider:
In your app/Providers directory, create a new file called GoogleAuthProvider.php. This file will contain the code for your custom authentication provider. Here's an example of what it might look like:
namespace App\Providers;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Http;
class GoogleAuthProvider extends \Tymon\JWTAuth\Providers\GoogleAuthProvider
{
public function redirectToGoogle()
{
return route('auth.login');
public function handleGoogleCallback()
{
$user = $this->getUser();
// Save the user to the database
auth()->login($user);
// Redirect the user back to the application
return redirect()->intended(route('home'));
}
}
4. Configure the JWT authentication middleware:
In your config/auth.php file, you will need to configure the JWT authentication middleware. Here's an example of what it might look like:
'middleware' => [
// ...
\Tymon\JWTAuth\Facades\JWTAuth::class,
],
5. Use the SSO functionality:
Once you have set up the authentication system and middleware, you can use the SSO functionality in your application. For example, you might use the auth()->user() method to retrieve the currently authenticated user, or use the Auth::check() method to check if a user is authenticated.
6. Implement the login and logout routes:
You will also need to implement the login and logout routes in your application. For example:
Route::get('/login', function () {
return view('auth.login');
});
Route::post('/login', 'LoginController@login');
Route::get('/logout', function () {
auth()->logout();
return redirect()->intended(route('home'));
});These are the basic steps for implementing single sign-on with Laravel. Of course, there are many other configuration options and customization possibilities, but this should give you a good starting point.